Curcumin Depression and Anxiety Benefits: New Research

Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, is gaining attention as a natural support for mental health. At Landys Chemist, our pharmacists closely follow emerging research into curcumin supplements and their potential to help manage stress-related mood changes. A recent chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) study found that curcumin helped reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety in preclinical models. Participants exposed to prolonged stress showed improved mood-related behaviours, reduced anxiety-like symptoms and healthier brain chemistry after taking curcumin.
These findings, published in SSRN and supported by other research, reinforce earlier evidence that curcumin’s anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective effects may help regulate mood. While large-scale human trials are still needed, curcumin is emerging as a promising natural option for supporting mental wellbeing.
Highlights:
- Curcumin may reduce depression and anxiety symptoms by targeting inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotransmitters
- Latest research using the CUMS model supports earlier studies on turmeric and mental health
- Safe and well-tolerated in most adults
What is Curcumin?
Curcumin is the main bioactive compound in turmeric (Curcuma longa), a golden spice used in Ayurvedic medicine for centuries. Known for reducing inflammation and protecting brain cells from oxidative damage, new research on curcumin signals its potential to support mood balance and emotional resilience.
How Curcumin May Help with Depression and Anxiety
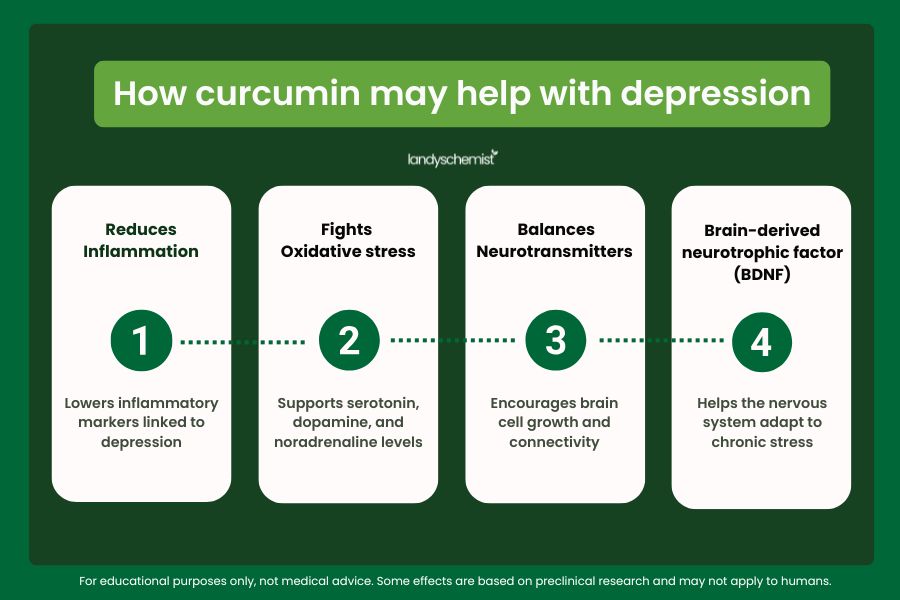
Recent studies, including the CUMS research, suggest curcumin could help in several ways:
- Modulating neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine and noradrenaline
- Reducing brain inflammation linked to mood disorders
- Protecting neurons from stress-related damage
Neesha Desai, pharmacist at Landys Chemist, explains:
“Curcumin shows exciting potential for mental wellbeing because it works on several biological pathways at once. By calming inflammation and supporting neurotransmitter balance, it may help the brain better cope with stress.”
What is Curcumin Used For?
Historically, turmeric and curcumin have been used to:
Today, researchers are exploring its role in cardiovascular health, metabolic balance, cognitive performance, and anxiety and depression.
Forms of Curcumin Supplements
For better absorption, curcumin supplements are available in:
- Standard capsules or tablets: a convenient daily option
- Nano-curcumin: tiny particles designed for higher bioavailability which you can get with Terranova’s NextGen CurcuSol Curcumin Complex
- Phytosomal and liposomal formulas: advanced delivery systems for improved absorption such as Lipolife LLT1 Liposomal Curcumin
How to Take Curcumin
Studies on mood-related benefits typically use 250mg–1500mg of curcumin daily for several weeks or months.
- Take with meals to improve absorption
- Consider bioavailability-enhanced forms
- Consistency is key for best results
Can Curcumin Treat Other Conditions?
Evidence suggests curcumin may also support arthritis management, metabolic health and brain ageing. However, more large-scale human studies are needed before it can be considered a treatment.
Is Curcumin Safe?
Yes, curcumin is generally considered safe and well tolerated in adults, even at high doses. However, caution is advised for:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Children
- People taking blood-thinning medication
Always seek medical advice before use.
Curcumin FAQs
How long does it take for curcumin supplements to affect mood?
In most clinical studies, noticeable mood benefits appear after consistent daily use for 6–12 weeks. Faster results are less common, as curcumin works gradually through anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective pathways.
Is curcumin safe to take with antidepressants?
Curcumin is generally well tolerated, but it can interact with certain medications, including antidepressants and blood thinners. Always check with your GP or pharmacist before combining them.
What type of curcumin supplement is best for mental health?
Bioavailability-enhanced forms, such as nano-curcumin or phytosomal curcumin, are often recommended as they deliver more active compounds to the brain compared to standard powders or capsules.
Can I get enough curcumin from turmeric in food?
Turmeric powder contains only about 3–5% curcumin, so it’s difficult to reach the studied doses (250–1500mg curcumin per day) through diet alone. Supplements are usually needed for better effects.
Is curcumin the same as cumin?
No. Curcumin comes from turmeric, while cumin is a different spice from the Cuminum cyminum plant.
Is turmeric the same as curcumin?
No. Turmeric is the whole root, and curcumin is one of its main active compounds. Read more here: The difference between turmeric and curcumin
Summary
Recent research suggests curcumin may help support mental health, easing symptoms of depression and anxiety. It works by reducing inflammation, protecting brain cells, and balancing neurotransmitters. The latest 2025 CUMS study shows potential benefits for mood, stress resilience, and emotional wellbeing. Available in enhanced-absorption supplement forms, curcumin is generally safe, though more large-scale human trials are needed.
Take a look at our range of natural supplements to support mood balance here
Sources:
- Curcumin Alleviates Depression via Multitarget Mechanisms and Neural Circuit Repair: Evidence from CUMS Model and fMRI Analysis - https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5360546
- Curcumin for depression: a meta-analysis - PubMed - https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31423805/
- Potential Therapeutic Benefits of Curcumin in Depression or Anxiety induced by chronic diseases: A Systematic Review of Mechanistic and Clinical Evidence - https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1638645/abstract
- Efficacy and safety investigation of LIMAN technology based curcumin formulation on knee osteoarthritis: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial - ScienceDirect - https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876382025000824
- Curcumin Supplementation Improves Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Women with Severe Obesity: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial-A Pilot Study - PubMed - https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40647170/
- Research trajectory and future trends in curcumin related to immunity: a bibliometric analysis of publications from last two decades - PMC - https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11973075/
- Curcumin supplementation improves the clinical outcomes of patients with diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk | Scientific Reports - https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-09783-5
- Curcumin for Inflammation Control in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial - PubMed - https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40573083/
- The effect of curcumin supplementation on cognitive function: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis - PubMed - https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40308636/
- The effect of curcumin on postpartum depression and anxiety in primiparous women: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial - PubMed - https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40281561/
Medically Reviewed & Authored By
This article was medically reviewed by Girish Desai, Chief Pharmacist at Landys Chemist since 1982 (GPhC Reg. No. 2019217), with expert nutritional input from Mitesh Desai, Head of Nutrition at Landys Chemist.
Written and compiled by Rhysa Phommachanh, Head of Digital at Landys Chemist and specialist in health and wellbeing content strategy.
Disclaimer: This content is grounded in current NHS guidance, clinical research, and expert pharmacy and nutrition knowledge to ensure accuracy and relevance for UK readers. For personalised advice, always consult your GP or a qualified health professional.