
Burnout: Symptoms, Prevention, and Advice
What is burnout?
Burnout is a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion that results from prolonged stress, often related to work or other demanding situations. Burnout is characterised by feelings of overwhelming fatigue, cynicism, detachment, and a sense of being unproductive or ineffective.
Burnout can affect anyone, but it is particularly common in people who are highly dedicated to their work or other activities, such as caregivers or students. According to a 2020 study by Gallup, 76% of employees experience burnout at work at least sometimes, with 28% reporting feeling burnt out very often or always.
Burnout can also lead to a range of physical and mental health problems, such as depression, anxiety, and physical illness.
There are five stages of burnout:
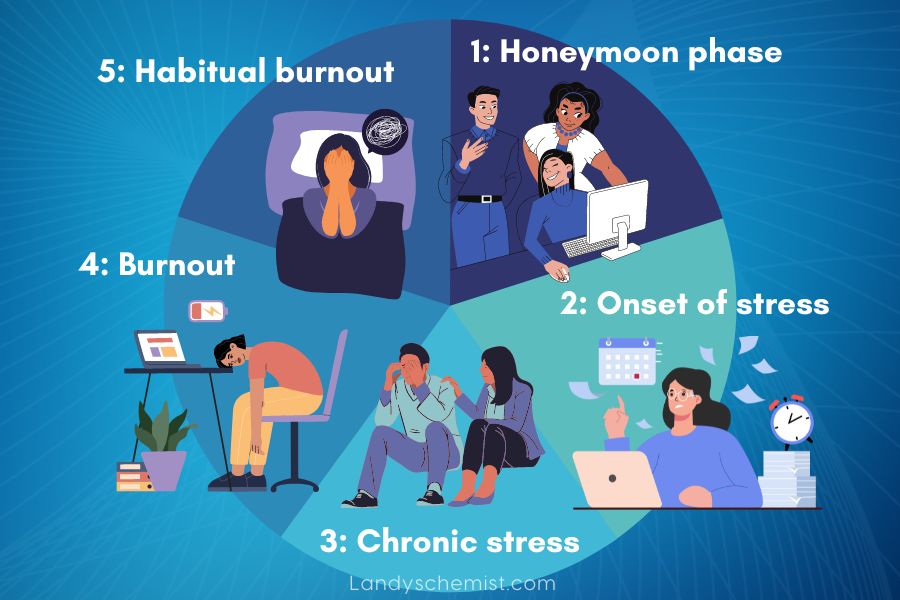
There are five stages of burnout that are widely recognised:
- The Honeymoon Phase: This is the initial stage, characterised by enthusiasm, high energy, and a strong sense of purpose. During this phase, individuals are excited about their work or other activities and feel motivated to take on new challenges.
- The Onset of Stress: As the demands and pressures of work or other activities increase, you may start to feel overwhelmed and experience stress. Common symptoms are feelings of frustration, irritability, and trouble sleeping.
- Chronic Stress: As stress persists, individuals may start to experience physical symptoms, such as headaches or gastrointestinal problems, as well as emotional symptoms, such as anxiety or depression. They may begin to withdraw from social activities and have difficulty concentrating.
- Burnout: At this stage, individuals feel a sense of emotional exhaustion and detachment from their work or other activities. They may feel cynical, disillusioned, and have a reduced sense of accomplishment. They may also experience physical symptoms, such as chronic fatigue or insomnia.
- Habitual Burnout: In the final stage, burnout becomes chronic and can lead to significant physical and mental health problems. Individuals may feel a sense of hopelessness and helplessness, and have difficulty functioning in their daily lives. They may experience more severe physical symptoms, such as chronic pain or illness, and may require medical or psychological intervention to recover.
Common signs of burnout:
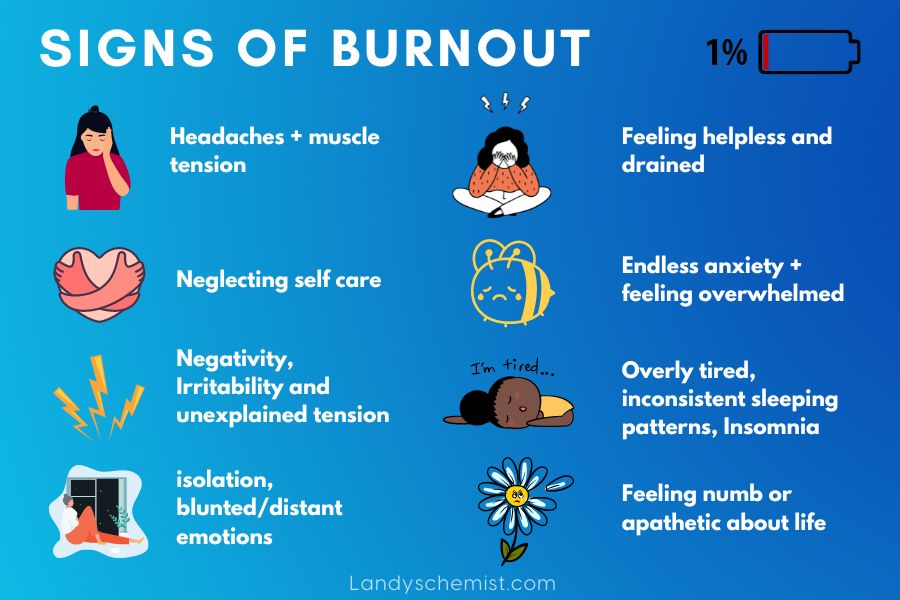
The symptoms of burnout can vary from person to person, but some common signs and symptoms include:
- Emotional exhaustion: feeling drained and depleted, lacking energy, and feeling emotionally drained.
- Detachment or cynicism: feeling detached from work or other activities, and developing a negative and cynical attitude.
- Reduced productivity: finding it hard to concentrate and be productive, and feeling like your work is no longer meaningful or valuable.
- Physical symptoms: experiencing physical symptoms like headaches, stomach aches, or a weakened immune system due to chronic stress.
- Changes in sleep patterns: either difficulty sleeping or oversleeping.
- Lack of motivation: feeling unmotivated and uninspired, and finding it difficult to get started on tasks or activities.
- Increased irritability: becoming more irritable, impatient, and easily frustrated with others.
It is important to note that experiencing some of these symptoms does not necessarily mean that someone is experiencing burnout. However, if these symptoms persist over an extended period and start to interfere with someone's daily life and functioning, it may be a sign that they are experiencing burnout. You can read more on spotting signs of burnout with the UK government civil service.
How To Prevent Burnout:

There are several steps you can take to prevent burnout:
- Set achievable goals and avoid setting unrealistic expectations for yourself.
- Allow yourself to take breaks throughout the day, take time off when needed, and prioritize getting enough rest.
- Develop a healthy work-life balance by making time for hobbies, exercise, and social activities outside of work or other responsibilities.
- Practice self-care by engaging in activities that promote mental and physical well-being.
- Seek support from friends, family, or colleagues.
- Maintain good communication with your colleagues, supervisors or family members to prevent any misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Learn how to prioritise your tasks and manage your time efficiently.
By taking these steps, you can help prevent burnout and maintain your overall well-being and productivity. It is also important to recognize the symptoms of burnout and seek help when needed.
How Long Does Burnout Last?
The duration of burnout can vary from person to person and depends on several factors, such as the severity of burnout, the causes of burnout, and the individual's coping strategies. In general, burnout can last for weeks, months, or even years if left untreated.
If the underlying causes of burnout are not addressed, the symptoms may continue to persist or even worsen over time.
However, with proper treatment and self-care, it is possible to recover from burnout and prevent its recurrence. Seeking support from a mental health professional, engaging in self-care activities, and making lifestyle changes can all help to alleviate burnout symptoms and promote recovery.
What Happens When You Can’t Take Time Off Work To Recover?
We understand that taking time off isn’t an easy option for many individuals, however there are some ways to make you work life easier:
- Speak to your employer: Have a conversation with your employer about your burnout and how it is making you feel. Discuss ways in which your day-to-day work life can change to avoid feeling overwhelmed. Consider whether tasks could be delegated to other team members whilst your recover, agree on frequent short breaks, or organise your tasks in a better way.
- Seek help from other sources: The UK Government has a Health and Safety Executive site which provides you a list of ways in which your employer must do to control work related-stress. You can also find other tips that will help manage your burnout. Additionally, consider reaching out to a therapist or support group for help managing stress and burnout.
- Prioritise self-care: In cases where you cannot get time off, you should focus on indulging in self-care around the hours you aren’t working. Train your mind to switch off work when you shift is over, and focus on hobbies and activities that boost your serotonin levels.
- Take supplements to help relieve stress: At Landys chemist we have a whole range of vitamins and supplements that help to tackle signs of stress and anxiety. You can explore them here. We recommend the following:
L-tryptophan is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation and stress management. By increasing serotonin levels, L-tryptophan supplementation can help reduce symptoms of stress and improve mood.
Ashwagandha is an adaptogenic herb that can help the body cope with stress by regulating the stress response and reducing cortisol levels. It has been shown to improve stress-related symptoms such as anxiety, fatigue, and sleep disturbances.
By Girish Desai, Pharmacist
*The claims are based on clinical research, are not aimed to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Food supplements should be used within the framework of a healthy lifestyle and not used as substitutes of a varied and balanced diet.





